Suspension
Suspension Polymerization of VCMs and the Role of PVOH
Water-soluble polymers are commonly used as dispersing stabilizers for suspension polymerization of vinyl chloride. In particular, various types of PVOH are used for a wide range of control of the surface activity of vinyl chloride monomers (VCMs) through polymerization and saponification.
Suspension polymerization of VCMs is a technique used to produce polyvinyl chloride (PVC) with a particle size of 50 to 200 μm. A VCM is suspended in water by means of stirring and the use of a dispersing agent, and then polymerizing it for several hours to achieve PVC. The properties of the resultant PVC powder, including the size and shape of particles and bulk density, vary depending on the particle forming process during polymerization.
In the particle forming process, the role of PVOH, which determines 50% to 80% of the properties of PVC powder, is extremely critical.
In recent years, high-speed polymerization has been progressing due to improved heat removal ability during suspension polymerization of vinyl chloride, and there is a need for PVOH that can meet both productivity and environmental protection without compromising residual VCM removal and other PVC properties.
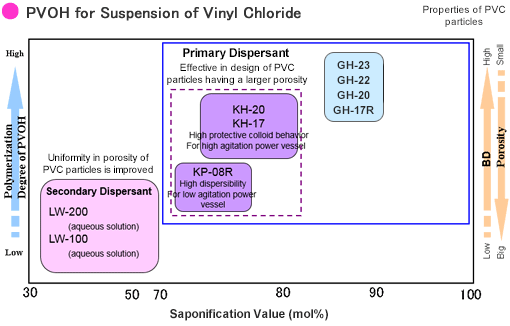
To respond to a wide range of requests from the market, Mitsubishi Chemical offers a full line of proprietary dispersants for suspension polymerization of VCMs (i.e. primary and secondary dispersants) that have a variety of surface-active properties.
Role of PVOH
PVOH, which acts as a primary dispersant during the initial stage of polymerization (PVC polymerization rate of 10% or less), disperses VCM droplets and activates coalescence and redispersion. As a secondary dispersant, PVOH further accelerates coalescence and redispersion.
PVOH, as a primary dispersant after the middle stage of polymerization (PVC polymerization rate of 30% or more), moderately suppresses secondary aggregation.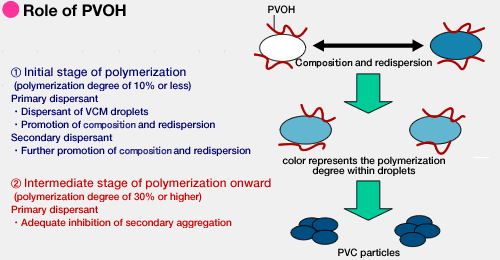
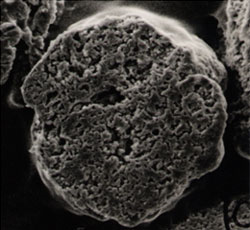
The photo below is a cross-sectional photo of PVC suspension polymerized particles.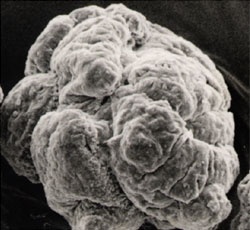
The figure below indicates the grades, degree of saponification, viscosity, and properties of primary dispersants.
| Grade | Saponification Value (mol%) | Viscosity *1 | Properties |
| GH-22 | 86.5-89.0 | 45-52 | For high BD |
| GH-20 | 86.5-89.0 | 40-46 | |
| GH-17R | 86.5-89.0 | 27-33 | |
| KH-20 | 78.5-81.5 | 44-52 | Good polymerization stability |
| KH-17 | 78.5-81.5 | 32-38 |
*1: 4% aqueous solution at 20°C
The figure below indicates the grades, degree of saponification, viscosity, and properties of secondary dispersants.
| Grade | Product form | Saponification Value (mol%) | Viscosity *1 (mPa・s) | Properties |
| LW-100 | 39-41% aqueous solution | 39.0-46.0 | 500-2,500 | Improving the uniformity of porosity |
*1: Viscosity measured with a 39–41% aqueous solution at 25°C
PVOH for PVC suspensions can be classified as shown in the diagram below based on the degree of PVOH polymerization and the characteristics of the PVC particles.