Emulsifiers
Application as emulsifiers
Features of GOHSENOL™ in Emulsifier Applications
Having both hydrophobic and hydrophilic groups within its molecular structure, GOHSENOL™ performs excellently as an emulsifier for synthetic resin emulsions.
In particular, it has the following three advantages over other surfactants on the market.
1. Favorable protective colloid properties
2. Resilience of dried films
3. Adhesion to hydrophilic materials such as cellulose
For these three features, GOHSENOL™ is preferred as a polymerization emulsifier for vinyl acetate and acrylic emulsions.
Emulsions Obtained by Using GOHSENOL™ as an Emulsifier
Emulsions obtained by using GOHSENOL™ as an emulsifier have the following three features.
1. G Type (partially saponified PVOH): Viscosity stability, high thixotropy, and high viscosity of the emulsion
2. N Type (fully saponified PVOH): Adds water resistance to the emulsion film and low thixotropy
3. A Type (quasi-fully saponified PVOH): Characteristics between those of the two types above (combination of water resistance and viscosity stability)
PVOH for vinyl acetate emulsions are classified as follows based on the water resistance and viscosity stability of the emulsion.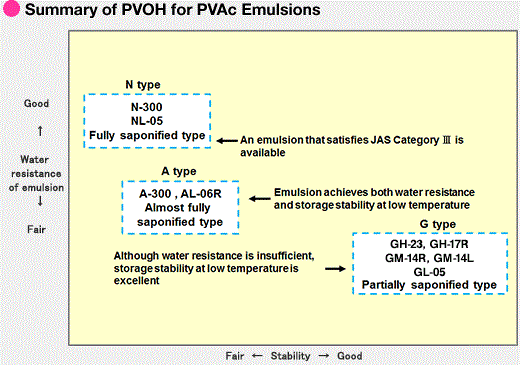
The figure below indicates the water resistance of emulsion films based on the elution ratio and degree of saponification of PVOH.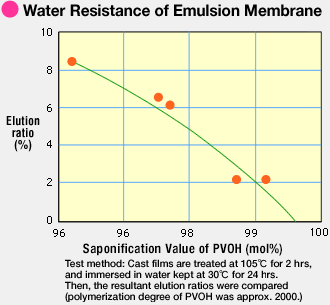
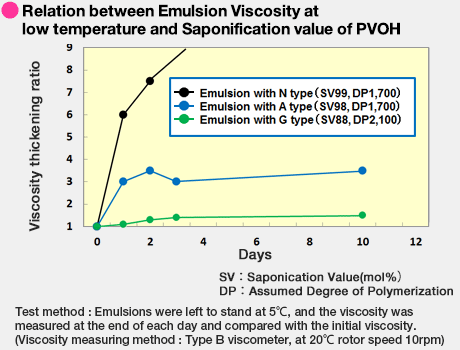
The figure below indicates the relationship between emulsion viscosity at low temperature and the degree of saponification of PVOH for each type of GOHSENOL™.